Models of prognosis of time series: proposal for aeronautical logistic support for the super tucano fleet
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18667/cienciaypoderaereo.525Keywords:
Demand, Forecast, Inventories, Logistic Support, Residual Error, Time SeriesAbstract
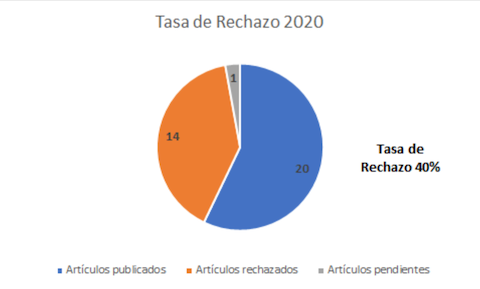
The prognosis becomes indispensable in any productive organization, considering that it is the basis of long-term planning in any functional area and therefore a vital tool for management decision-making. The art of forecasting aims to predict the demand for a product or service in such a way that the productive system is efficient and responds to the needs in quantity and opportunity. In the first instance, this article makes a bibliographic tour to describe the context of the forecast, then a documentary revision is carried out in terms of projections of various industrial sectors, and finally the particularity of the forecast is presented in the Colombian Air Force specifically with a proposal for the projection of the demand of the aeronautical logistic support of the fleet of the Super Tucano A-29 team in Combat Air Command No. 2; concluding that the suggested methodology is not far from the current trends and on the contrary brings together most of them, selecting the best model independently for each component of the fleet, a fact that guarantees a correct inference and that when meeting the established conditions can be extrapolated and standardized for the aeronautical logistic support of the Colombian Air Force, a situation that if presented would generate a high budgetary impact for the Air Force, for the Ministry of Defense and therefore for national public finances, because the costs of logistic support would reflect a decrease from previous periods.Downloads
References
Anderson David R, S. D. (2005). Estadistica para Administracion y Economia . Mexico DF: Thomson.
Bernanke, & Boivin. (2003). Monetary Policy in a Data-rich Environment. Journal of Monetary Economics, 525-546.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3932(03)00024-2
Bernanke, B., Boivin, J., & Eliazs, P. (2005). The Quarterly Jorunal of Economics, 387-422.
https://doi.org/10.1162/qjec.2005.120.1.387
Bourgeois, J., & Barnes, J. (1979). Does Advertising Increase Alcohol Consumption? Journal of Advertising Research, 19-29.
Bratina, D., & Faganel, A. (2008). Forecasting the Primary Demand for a Beer Brand Using Time Series Analysis. Organizacija,Volume 41, Number 3,.
https://doi.org/10.2478/v10051-008-0013-7
Brubaker, K., & McCuen, R. (1990). "Level of significance selection in engineering analysis. Journal of Professional Issues in Engineering ASCE Vol. 116 No. 4,, 375-387.
https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1052-3928(1990)116:4(375)
Chase Richard B., A. N. (2000). Administracion de Produccion . Santa Fe De Bogota: Mc Graw Hill.
Dekimpe, M., & Hannsens, D. (1995). The Persistence of Marketing Effects on Sales. Marketing Science, 1-21.
https://doi.org/10.1287/mksc.14.1.1
Demirov, E., & Pinardi, N. (2002). Simulation of the Mediterranean Sea circulation from 1979 to 1993: Part I. The interannual variability, 33-34, 23-50.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-7963(02)00051-9
Dobricic, S. P. (2006). Daily oceanographic analyses by the Mediterranean basin scale assimilation system. Ocean Sci. Discuss., 3, 1977-1998.
https://doi.org/10.5194/osd-3-1977-2006
Dominick, S. (2009). Microeconomia. Mexico DF: Mc Graw Hill.
Fragkakis, N., Lambropoulos, S., & Pantouvakis, J. (2010). A cost estimate method for bridge superstructures using regression analysis and bootstrap. Organization, technology and management in construction. An international journal, 182-190.
Franke, G., & Wilcox, G. (1987). Alcoholic Beverage Advertising & Its Impact on Model Selection. Applied Mathematics & Computation 34 (November), 22-30.
https://doi.org/10.1080/00913367.1987.10673082
Franses, P. (1991). Primary Dem& for Beer in The Netherl&s: An Application of ARMAX Model Specification. Journal of Market research 28, 240-245.
https://doi.org/10.1177/002224379102800212
Gouviea N. and Fletcher T. (2000). Time series analysis of air pollution and mortality: Effects by cause, age and socioeconomic status. J. Epidemiol. Commun. H., 54, 750-755.
https://doi.org/10.1136/jech.54.10.750
Gujarati, D. (1999). Essentials of Econometrics. New York: Irwin Mc Graw Hill.
Hegazy, T., & Ayed, A. (1998). Neural network model for parametric cost estimation of highway projects. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, Vol. 124 No.3, 210-218.
https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9364(1998)124:3(210)
Herzberg, A., & Frew, L. (2003). Can public policy be influenced? Environmetrics, 14, 1-10.
https://doi.org/10.1002/env.556
Hoyos Gomez, F. (Mayo de 2014). Presentacion PASLO CACOM-2 2014. Apiay, Meta, Colombia.
Keane, M. (1997). Modeling Heterogeneity & State Dependence in Consumer Choice Behaviour. Journal of Bussiness & Economic Statistics, 310-327.
https://doi.org/10.1080/07350015.1997.10524709
Klemm, O., & Lange, H. (1999). Trends of air pollution in the Fichtelgebrige Mountains, Bavaria. Environ Sci. &Pollut, 193-199.
https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02987325
Konstantinidis, D., & Maravas, A. (2003). Egnatia Motorway concrete bridges statistics. ASECAP Study and Information Days proceedings of the international conference in Portoroz Slovenia, 92-109.
Kyriakidis, J. (2001). Stochastic modeling of atmospheric pollution: a spatial time series framework. Part II: application to monitoring monthly sulfate deposition over Europe. Atmos Environ 35, 2339-2348.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(00)00540-9
Lanteri, L. (2010). Economia Vol XXXIII, No. 66.
Lee, C. k. (2002). Multifractal characteristics in air pollutant concentration time series. Water Air Soil Poll. 135, 389-409.
https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014768632318
Leeflang, & Van Dujin, J. (1982). The Use of Regional Data in Marketing Models:The Dem& for Beer in The Netherl&. European Research 10, (January): 29-40.
Litterman, R. (1985). Forecasting with Bayesian Vector Autoregressions-five Years of Experience. Minneapolis: Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis.
Lucas, R. (1976). Econometric Policy Evaluation: a critique. New York: En Brunner K y A Meltzer.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2231(76)80003-6
Lucas, y. S. (1979). After Keynesian Macroeconomics. Minneapolis: Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis..
McKee, D. (1993). Health effects associated with ozone and nitrogen dioxide exposure. . Water Air Soil Poll, 11-35.
https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00480811
Mobley, K. (1999). Root Cause and failure analysis. United of States of America: Butterworth-Heinemann.
Modarres, R., & Khosravi Dehkordi, A. (2005). Daily air pollution time series analysis of Isfahan City. Int. J. Environ. Sci Tech, 259-267.
https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325885
Murphy, A. (1988). Skill score based on the mean square error and their relation to mthe correlation coefficient. Monthly weather review, 2417-2424.
https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1988)116<2417:SSBOTM>2.0.CO;2
Murphy, A. (1993). What is a good forecast? Weather forecasting, 281-293.
https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0434(1993)008<0281:WIAGFA>2.0.CO;2
Pinardi, N. A. (2003). The Mediterranean ocean Forecasting System: First Phase of implementation (1998-2000).
https://doi.org/10.5194/angeo-21-3-2003
Geophisicae, vol.21, 189-204.
Prescott, E. (1977). Should Control Theory be usde for Economic Stabilization. New York: Brunner, K y A Meltzer.
https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2231(77)90017-3
Roberts, S. (2003). Combining data from multiple monitors in air pollution mortality time series studies. Atmos. Environ., 37, 3317-3322.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(03)00289-9
Salcedo, R., Alvim Ferraz, M., Alves, C., & Martins. (1999). Time series analysis of air pollution data. Atmos. Environ., 33, 2361-2372.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(99)80001-6
Schwartz, J., & Marcus, A. (1990). Mortality and air pollution in London: a time series analysis. Am. J. Epidem., 131, 85-194.
https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115473
Seetharaman, P. (1999). Investigating Household State Dependence Effects across categories. Journal Of Market Research, 488-500.
https://doi.org/10.1177/002224379903600407
Sims, C. (1992). Interpreting the Macroeconomic Time Series Facts: the effects of monetary policy. European Economic Review, 975-1000.
https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-2921(92)90041-T
Skamris, M., & Flyvbjerg, B. (1997). Inaccuracy of traffic forecasts and cost estimates on large transport projects. Transport Policy, Vol. 4 No. 3, 141-146.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0967-070X(97)00007-3
Theil, H. (1971). Principles of Econometrics. Nueva York: J. Wiley.
Tonani, M. (2007). A high resolution free surface model on the Mediterranean Sea. Ocean Sci. Discuss.
https://doi.org/10.5194/osd-4-213-2007
Tonani, M., Pinardi, N., Fratianni, C., & Dobricic, S. (2007). Forecast and analysis assessment through skill scores. Oceans Science Discussions, 189-212.
https://doi.org/10.5194/osd-4-189-2007
Touloumi G., A. R. (2004). Analysis of health outcome time series data in epidemiological studies. Environmetrics, 101-117.
https://doi.org/10.1002/env.623
Voigt, K., & Bruggemann, R. (2004). Data analysis of environmental air pollutant monitoring systems in Europe. Environmetrics, 15, 577-596.

Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Assignment of Copyrights
Authors assign Ciencia y Poder Aéreo journal the exclusive rights (reproduction, distribution, public communication, and transformation) to exploit and commercialize their work, in whole or in part, in all the formats and modalities of present or future exploitation, in all languages, throughout the life of the work and throughout the world.
All contents published in Ciencia y Poder Aéreo journal are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, whose complete information is available at http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
Under the terms of this license, users are free to download, print, extract, archive, distribute and publicly communicate the content of articles, provided that proper credit is granted to authors and Ciencia y Poder Aéreo, scientific journal of the Graduate School of the Colombian Air Force. Except when otherwise indicated, this site and its contents are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
For other uses not considered under this license it is required to contact the Director or the Editor of the journal at the e-mail address cienciaypoderaereo1@gmail.com.
The Graduate School of the Colombian Air Force and this publication are not responsible for the concepts expressed in the articles, including the metadata or the affiliation stated by authors. This is the full responsibility of the authors.